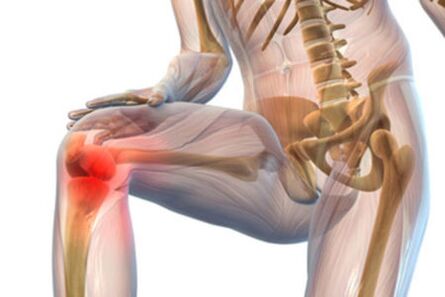
Arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) is a degenerative lesion of the joint, which eventually leads to its deformation. In it, cartilage tissue begins to collapse. Gradually, the functionality of the knee is impaired and the patient loses the ability to move normally. This disease is very common.
The treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee is long-term, but it cannot provide a complete cure for the problem. However, therapy is necessary to preserve joint mobility and functionality as much as possible, in addition to improving the patient's quality of life.
Types of diseases
It is possible to classify the knee joint gonarthrosis by the reasons of its development. It's primary and secondary. The first type of illness occurs most often. It also has another name - idiopathic osteoarthritis. The exact reason for the development of this form of knee arthrosis is difficult to establish, as there are many influencing factors.
The secondary type of pathology is clearly linked to one reason or another. For example, it usually occurs after a knee injury due to great physical strain on the knee joint. This gonarthrosis is often genetically determined. Certain diseases can also cause dystrophic changes in the knee joint: diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, congenital deformity of the lower extremities.
Why the pathology develops
The knee joint is one of the most complex joints in the human body. It is formed by the femur, tibia and patella. The joint also includes triangular cartilage with curved edges - menisci. The well-coordinated work of the knee is ensured by the musculoskeletal system. Almost all bone surfaces of the joint are covered by cartilage tissue, which is about 0. 5 cm thick, which feeds on blood vessels as well as diffusely (obtaining useful substances from synovial fluid).
The cartilage in the knee allows the bony surfaces to slide and protect them. If the nutrition of this tissue is disturbed, dystrophic processes start in it, it becomes thinner. If left untreated, the cartilage completely disappears and the knee joint stops moving. The reason for the development of osteoarthritis may be different. For example, the following factors can cause the appearance of a secondary form of pathology:
- Excessive stress on the knee joint. In that case, changes can occur that the person is not even aware of. Therefore, the load should be moderate, especially in old age. The biggest damage comes from crouching and running on hard surfaces (asphalt).
- Knee injury. This can include damage to the meniscus, dislocation of the joint, fracture. This reason contributes to the development of the disease in young people. After repairing the limb, the blood circulation in the limb deteriorates. Damage or removal of the menisci in 90% of cases lead to arthrosis.
- Too much body weight. Excessive weight can damage the menisci. Knee joint restoration is time-consuming and difficult. In obese people, bilateral knee arthrosis often occurs. An additional downside is the presence of varicose veins. In this case, the patient develops the most severe form of knee gonarthrosis.
- Weakness of the ligament apparatus. Because of this, there is a very high joint mobility. Although a person can sit on the wire without any problems even without heating, at this point the joint receives microtrauma. If the knee is damaged enough, arthrosis begins to develop.
- Violation of metabolic processes. In this case, the knee joint does not receive enough nutrients.
- Joint pathologies. The presented pathology may be caused by arthritis of the knee joint (reactive, rheumatoid). It is characterized by the development of inflammation and accumulation of a lot of fluid in the joint cavity. The cartilage tissue in the knee begins to deteriorate.
- Stressful situation. Mood changes, the constant presence of the nervous system in a state of tension, can cause arthrosis of the knee joint.
- Congenital diseases of muscles, ligaments and dysplasia.
- Chondrocalcinosis (premature deposition of calcium salts in the cartilage of the knee). The pathology is systemic.
- Osteomyelitis. It is an inflammation of the bone marrow, in which purulent masses form. They negatively affect surrounding tissues. Over time, the purulent masses go beyond the bone in the knee joint. Lack of treatment threatens the development of sepsis.
- Acromegaly. This is an endocrine disorder in which the level of growth hormone - growth hormone - increases. Most often, a benign tumor in the anterior pituitary gland contributes to an increase in its number. If such a disease develops during adolescence, the child develops a specific physique. The overgrowth rate of cartilage tissue leads to deformation of the knee joint.
- Diabetes.
- Hypothyroidism. This disease is also endocrine. This is due to a lack of thyroid hormones. A person's mass starts to increase, he moves little, and the cartilage in the knee joint wears away.
- Cold burn. In this case, ice crystals form in the soft tissue, which kills living cells.
- Synovitis (inflammation located in the synovial pocket of the joint).
All these reasons are capable of causing gonarthrosis in the knee, while the person will not even notice when the disease has started to develop.
What stages does arthrosis go through in its development?
The effectiveness of knee treatment depends on the degree of development of the diagnosed arthrosis in the patient:
- First degree of knee arthrosis. Pain at this stage is not much felt. The patient can endure discomfort for years, without rushing to contact specialists or undergo any type of treatment. A person needs help during an exacerbation. The acute onset of pain is not typical of knee arthrosis.
- Arthrosis of the 2nd degree knee joint. The intensity of the discomfort increases. Pain occurs not only after physical exertion on the knee joint, but also at rest. To get rid of unpleasant sensations, you need more rest. In the area of the knee joint, a swelling appears, the patient hears a snap. The x-ray shows a narrowing of the joint space, a slight deformation of the knee joint.
- Arthrosis of the 3rd degree knee joint. In this case, the mobility of the knee is severely limited, and sometimes the leg cannot fully straighten. Joint pain becomes intense and constant, and appears as a response to changing weather conditions. Discomfort is painful in nature and is difficult to get rid of at rest. The patient's sleep is often disturbed and, to alleviate his condition at least a little, he uses NSAIDs. A person develops lameness and joint deformity is very noticeable.
Treatment of osteoarthritis should be started as soon as possible, before bone tissue destruction becomes critical. In case of irreversible changes, only surgery will help the patient.
Knee Arthritis Symptoms
The development of arthrosis does not occur overnight. As it progresses, symptoms become more intense. For gonarthrosis, the following manifestations are characteristic:
- A snap is a snap that is heard with a certain movement. The patient may notice this symptom very late. However, he says that the joint surfaces are damaged, ridges and bony bulges have appeared.
- Swelling and swelling of the knee.
- Painful sensations. In the first stage of osteoarthritis development, they are invisible and can only appear after severe static load on the knee joint. Dynamic exercise, in turn, improves the condition of the joint, its nutrition and subsequent prognosis. As the top layer of cartilage is effaced in arthrosis, the nerve endings are exposed. After some time (after resting), the fibers are covered with a small layer of fibrin and are less sensitive - the pain in the knee goes away. If the knee joint continues to collapse, the discomfort will not even let the person rest. Edema appears in the bursa, which further compresses the nerves. The inflammatory process begins.
- Restricted mobility. This symptom makes it possible to differentiate arthrosis from other pathologies of the knee joint. The stiffness appears in the morning after sleep and disappears after half an hour. If this condition lasts longer, it indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Decreased range of motion. The patient is unable to straighten the limb all the way. As the patient is in constant pain, he tries to reduce his range of motion and the ligaments adapt to this. That is, they are shortened and do not allow the knee joint to fully fulfill its function.
- Seam binding. It arises as a result of a strong change in articular surfaces.
- Dislocations and subluxations. They appear in the last stage of the development of arthrosis, when the joint is severely deformed.
Over time, the person experiences muscle atrophy, proliferation of osteophytes, and weakening of the lateral ligaments. The consequences of osteoarthritis are serious, as the person is incapacitated.
How to define arthrosis correctly?
To start the correct treatment of arthrosis, the patient must undergo a thorough examination. The diagnosis must be differential and include the following studies:
Thanks to these diagnostic measures, specialists can accurately determine knee arthrosis and prescribe a truly effective treatment.
Knee arthrosis treatment
The treatment of osteoarthritis must be versatile and long-term. As it will not be possible to completely stop the destruction of the joint, therapy must be carried out constantly to improve the patient's quality of life.
Medicines in the treatment of arthrosis
The doctor can prescribe the following medications:
- Non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used in the form of pills and ointments. However, in case of severe pain syndrome, which cannot be eliminated by conventional methods, an injection is used. It helps to quickly soothe pain, relieve swelling and reduce the intensity of inflammation. These remedies can only eliminate the symptom, but they cannot cure osteoarthritis. Only a doctor should prescribe these funds. The course of treatment lasts no longer than 14 days, and relief comes within 2-3 days.
- Chondroprotectors for arthrosis of the knee joint. Each of these drugs contains useful substances that can regenerate cartilage. However, it will only be effective if your application is launched on time. If the cartilage is completely erased, the use of chondroprotectors will be useless. Treatment with these means will be long term (at least 6 months). Pills and topical medications are the most commonly used, although injections are possible.
- Vasodilators. They help relieve spasm and pain syndrome, restore normal blood circulation, and improve nutrition in the knee joint.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Most of the time, they are used in the most difficult cases, when other drugs do not have a positive effect. Intra-articular injections in the knee are used for osteoarthritis. They can only be used once a year.
- Enzymes. They provide regeneration of the cartilage structure in the early stages of development of knee arthrosis. They are also prescribed for injection into the joint.
- Hyaluronic acid. Provides smooth movement of the knee joint as it is able to replenish synovial fluid.
- Local preparations - ointments, creams, gels. They also just alleviate symptoms.
- Medication Compresses. In this case, a drug is used that can penetrate the skin, helps to eliminate muscle pinches and has a reabsorbing effect. The compress can be made with medicinal bile.
Drug therapy in the treatment of arthrosis is essential. However, medications must be used strictly in the dosage prescribed by the doctor. It is impossible to independently increase or decrease the rate, change the daily rate without the knowledge of an expert.
Characteristics of physical therapy treatment and exercise therapy
You can also treat arthrosis of the knee joint using physical therapy procedures:
- Massage. Helps restore normal blood circulation in tissues, eliminate muscle spasm.
- Drug electrophoresis eliminates inflammation in the joint and also produces an analgesic effect.
- Magnetic therapy. With the help of specific radiation, the tissues around the affected right or left joint are stimulated. Metabolic processes in cells are improved.
- UHF. The waves promote the production of synovial fluid, which lubricates the knee.
- Phonophoresis with corticosteroids.
- Electrotherapy helps to eliminate not only pain but swelling as well. <4_img_blockxx>
- Mud Therapy.
- Hirudotherapy.
- Shockwave therapy.
- Heat treatment. This includes paraffin therapy. Thanks to this procedure, local blood circulation is improved.
- SMV Therapy. This physiotherapy stimulates blood circulation, relieves swelling and helps improve cartilage tissue nutrition.
Physical therapy is extremely helpful. It is necessary to restore the elasticity of muscle tissue and ligaments, improve the mobility of the knee joint. The following exercises will be helpful:
The set of exercises is individually selected by the attending physician. Gymnastics is best done after a small massage with medicated ointments. Physical therapy is an additional effective method of treating arthrosis, which increases the effect of medications.
Is surgery necessary?
In the most difficult cases, when the joint is severely destroyed by arthrosis, the patient is prescribed an operation. There are several types of interventions:
It's best not to bring it in for surgical intervention. Treatment should start in the first phase of the development of arthrosis. Orthopedic devices will help to consolidate the result: a cane, an orthosis to reduce the load, knee braces with infrared radiation.
The use of folk remedies
The complete cure of arthrosis is impossible, as the degenerative process will gradually progress. However, you can eliminate the symptoms and stop the destruction of the knee joint in osteoarthritis. Folk remedies can be used during an exacerbation as well as during relative calm. But first you need an expert consultation. The following recipes will be useful for osteoarthritis:
Cabbage and burdock leaves help relieve inflammation in osteoarthritis. Folk remedies cannot be considered a panacea, but they enhance the effectiveness of other types of therapy.
Nutritional Rules for Arthrosis
The treatment of osteoarthritis does not require a particularly strict diet, but you should still follow some nutritional rules:
- Reduce your salt intake. Its total amount per day should not exceed 2 g. It is preferable to salt the dish immediately before using it and not during cooking.
- The amount of spices used during the treatment of osteoarthritis should also be reduced. The same applies to fermented foods, pickles. Marinades and canned food are generally better to exclude from the diet.
- Animal fats are not recommended.
- The menu must not contain sweets, pies and breads made with wheat flour. <5_img_blockxx>
- In arthrosis, alcohol and nicotine are strictly prohibited.
- Dishes with gelatine content are useful: gelatine gelatine, bone-in beef broths.
- It is important for osteoarthritis to consume milk proteins (products should not be fatty), fish, seafood.
- The diet should contain vegetable, vegetable and fruit oils, natural juices.
- A person must consume a sufficient amount of fluids per day.
The correct diet for osteoarthritis must be developed by an expert. You cannot go to extremes, even if the patient is overweight. Dramatic and inadequate weight loss will only worsen your health. In that case, treatment will be significantly delayed.
Arthrosis prevention
To avoid the possibility of developing arthrosis, as well as to not lose the ability to walk, it is necessary to follow the following expert advice:
- We must not forget the movement. Better to go to the pool, ride a bike, go hiking outdoors. You can also go to dances.
- It is advisable to avoid knee joint injuries and hypothermia, as this causes post-traumatic arthrosis.
- It is best to wear protective knee braces or other orthopedic devices for prolonged exertion.
- It is advisable to wear comfortable shoes. <6_img_blockxx>
- It's important to eat well - osteoarthritis won't stand a chance if all the necessary nutrients are regularly supplied to the joint.
- If you are overweight, you should get rid of it.
- It is better to avoid stress, as well as correctly organize the work and rest routine.
- It is necessary to strengthen the body's defenses.
- All inflammatory or infectious pathologies that can lead to the development of arthrosis must be eliminated over time.
Correct prevention can significantly delay joint destruction, which under normal conditions is a natural aging process in the body.
Arthrosis of the knee joint is an incurable disease, but its progression can be slowed down and even stopped with an improvement in quality of life.

























